TDCB-Prüfkörper
Erscheinungsbild
| Ein Service der |
|---|

|
| Polymer Service GmbH Merseburg |
| Tel.: +49 3461 30889-50 E-Mail: info@psm-merseburg.de Web: https://www.psm-merseburg.de |
| Unser Weiterbildungsangebot: https://www.psm-merseburg.de/weiterbildung |
| PSM bei Wikipedia: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polymer Service Merseburg |
TDCB-Prüfkörper
Die angelsächsische Abkürzung TDCB steht für "Tapered-Double-Cantilever Beam".
Prüfkörperform
In der Literatur [1–3] finden sich verschiedene Variationen der selben Grundform.
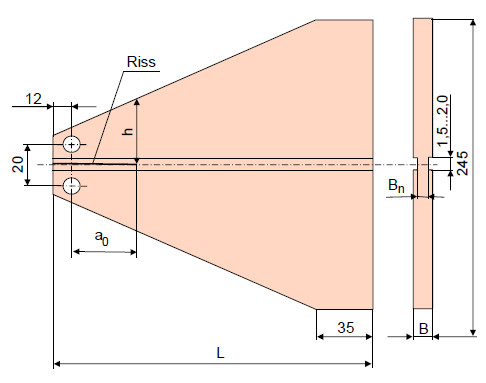
|
|
| Bild 1: | Schematische Darstellung des TDCB-Prüfkörpers |
Ermittlung von bruchmechanischen Kennwerten an TDCB-Prüfkörpern
Bestimmungsgleichung
| Fehler beim Parsen (SVG (MathML kann über ein Browser-Plugin aktiviert werden): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle K_I = 2F(\frac{m}{B \cdot B_{n}})^{\frac{1}{2}}} |
mit der Belastung durch Zugkraft F und:
| Fehler beim Parsen (SVG (MathML kann über ein Browser-Plugin aktiviert werden): Ungültige Antwort („Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.“) von Server „https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/“:): {\displaystyle m=\frac{1}{h}+\frac{3a^2}{h^3}} |
Eine umfangreiche Zusammenstellung von geeigneten Prüfkörpern für bruchmechanische Untersuchungen an Kunststoffen und Verbundwerkstoffen ist in Prüfkörper für bruchmechanische Prüfungen enthalten.
Literaturhinweise
| [1] | Blumenauer, H., Pusch, G.: Technische Bruchmechanik. Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie, Leipzig Stuttgart (1984) 1. Auflage, S. 109 und S. 146 (ISBN VLN 152-915/61/82; siehe AMK-Büchersammlung unter E 29-1) |
| [2] | Blumenauer, H., Pusch, G.: Technische Bruchmechanik. Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie, Leipzig Stuttgart (1987) 2. Auflage, S. 127–129 und S. 140 (ISBN 3-342-00096-1; siehe AMK-Büchersammlung unter E 29-2) |
| [3] | Brown, E. N., Sottos, N. R., White, S. R.: Fracture Testing of a Self-healing Polymer Composite. Experimental Mechanics 42 (2002), No. 4, 372–379 |
| [4] | Kobayashi, T., Broutman, L. J.: Fracture Studies in Rubber-modified Acrylics. 1 Experimental Method: Design of Sandwich-tapered Double-cantilever Beam Cleavage Specimens. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 17 (1973) 1909–1917 |
| [5] | Yaniv, G., Daniel, I. M.: Height-tapered Double Cantilever Beam Specimen for Study of Rate Effects on Fracture Toughness of Composites. In: Whitcomb, J. D. (Eds.): Composite Material: Testing and Design (Eight Conference), ASTM STP 972. ASTM, Philadelphia (1988), S. 241–258 |
| [6] | Hwang, J. H., Kwon, O., Lee, C. S., Hwang, W.: Interlaminar Fracture and Lowvelocity Impact of Carbon/Epoxy Composite Materials. Mechanics of Composite Materials 36 (2000) 117–130 |
| [7] | White, S. R., Sottos, N. R., Geubelle, P. H., Moore, J. S., Kessler, M. R., Sriram, S. R., Brown, E. N., Viswanathan, S.: Autonomic Healing of Polymer Composites. Nature 409 (2001) 794–797 |
| [8] | El-Bagory, T. M., El-Fadaly, M. S., Younan, M. Y. A., Abdel-Latif, L. A.: Influence of Crack Orientation and Crosshead Speed on the Fracture Toughness of PVC Pipe Materials. Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology – Transactions of the ASME 126 (2004) 489–496 |
Normenhinweis
- ISO 25217 (2009-05): Adhesives − Determination of the Mode I Adhesive Fracture Energy of Structural Adhesive Joints using Double Cantilever Beam and Tapered Double Cantilever Beam Specimens
Zusätzliche Literaturhinweise zur Anwendung von TDCB-Prüfkörpern:
Polymere und Polymerverbundwerkstoffe
- Daniel, I. M., Yaniv, G., Auser, J. W.: Rate Effects on Delamination Fracture Toughness of Graphite/Epoxy Composites. Composite Structures 4 (1987) 258–272
- Hwang, J. H., Lee, C. S., Hwang, W.: Effect of Crack Propagation Directions on the Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Carbon/Epoxy Composite Materials. Applied Composite Materials 8 ( 2001) 411–433
- Gamby, D., Delaumenie, V.: Measurement and Modelling of Crack Propagation Velocity in a Viscoelastic Matrix Composite. Composites Part A – Applied Science and Manufacturing 28 (1997) 875–881
- Li, G. Q., Meng, H., Hu, J. L.: Healable Thermoset Polymer Composite Embedded with Stimuli-responsive Fibres. Journal of the Royal Society Interface 9 (2012) 3279–3287
- Billiet, S., van Camp, W., Hillewaere, X. K. D., Rahier, H., Du Prez, F. E.: Development of Optimized Autonomous Self-healing Systems for Epoxy Materials Based on Maleimide Chemistry. Polymer 53 (2012) 2320–2326
- Jin, H. H., Mangun, C. L., Stradley, D. S., Moore, J. S., Sottos, N. R., White, S. R.: Self-healing Thermoset Using Encapsulated Epoxy-Amine Healing Chemistry. Polymer 53 (2012) 581–587
- Neuser, S., Michaud, V., White, S. R.: Improving Solvent-based Self-healing Materials Through Shape Memory Alloys. Polymer 53 (2012) 370–378
- Coope, T. S., Mayer, U. F. J., Wass, D. F., Trask, R. S., Bond, I. P.: Self-healing of an Epoxy Resin Using Scandium(III) Triflate as a Catalytic Curing Agent. Advanced Functional Materials 21 (2011) 4624–4631
- Brown, E. N.: Use of the Tapered Double-cantilever Beam Geometry for Fracture Toughness Measurements and its Application to the Quantification of Self-healing. Journal of Strain Analysis for Engineering Design 46 (2011) 167–186
- Li, H. Y., Wang, R. G., Liu, W. B.: Toughening Self-healing Epoxy Resin by Addition of Microcapsules. Polymer & Polymer Composites 19 (2011) 223–226
- Mangun, C. L., Mader, A. C., Sottos, N. R., White, S. R.: Self-healing of a High temperature Cured Epoxy Using Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Chemistry. Polymer 51 (2010) 4063–4068
- Brown, E. N., White, S. R., Sottos, N. R.: Fatigue Crack Propagation in Microcapsuletoughened Epoxy. Journal of Materials Science 41 (2006) 6266–6273
- Brown, E. N.: Microcapsule Induced Toughening in a Self-healing Polymer Composite. Journal of Materials Science 39 (2004) 1703–1710
- Kessler, M. R., Sottos, N. R., White, S. R.: Self-healing Structural Composite Materials. Composites Part A – Applied Science and Manufacturing 34 (2003) 743–753
- Meure, S., Wu, D. Y., Furman, S.: Polyethylene-co-methacrylic Acid Healing Agents for Mendable Epoxy Resins. Acta Materialia 57 (2009) 4312–4320
Polymere Adhesive
- Ebewele, R., River, B., Koutsky, J.: Tapered Double Cantilever Beam Fracture Tests of Phenolic-Wood Adhesive Koints. Wood and Fiber Science 11/3 (1979) 197–213
- Ebewele, R. O., River, B. H., Koutsky, J. A.: Tapered Double Cantilever Beam Fracture Tests of Phenolic-Wood Adhesive Joints: Part II. Effects of Surface Roughness, the Nature of Surface Roughness, and Surface Aging on Joint Fracture Energy. Wood and Fiber Science 12/1 (1980) 40–65
- Blackman, B. R. K., Hadavinia, H., Kinloch, A. J., Paraschi, M., Williams, J. G.: The Calculation of Adhesive Fracture Energies in Mode I: Revisiting the Tapered Double Cantilever Beam (TDCB) Test. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 70 (2003) 233–248
- Meiler, M., Roche, A. A., Sautereau, H.: Tapered Double Cantilever Beam Test Used as a Practical Adhesion Test for Metal/Adhesive/Metal Systems. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology, 13/7 (1999) 773–788
- Davalos, J. F., Madabhusi-Raman, P., Qiao, P. Z., Wolcott; M. P.: Compliance Rate Change of Tapered Double Cantilever Beam Specimen with Hybrid Interface Bonds. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics 29 (1998) 125–139
- Jin, H. H., Miller, G. M., Pety, S. J., Griffin, A. S., Stradley, D. S., Roach, D., Sottos, N. R., White, S. R.: Fracture Behavior of a Self-healing, Toughened Epoxy Adhesive. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives 44 (2013) 157–165
- Cho, J. U., Kinloch, A., Blackman, B., Sanchez, F. S. R., Han, M. S.: High-strain Fracture of Adhesively Bonded Composites Joints in DCB and TDCB Specimens. International Journal of Automotive Technology 13 (2012) 1127–1131
- Marzi, S., Biel, A., Stigh, U.: On Experimental Methods to Investigate the Effect of Layer Thickness on the Fracture Behavior of Adhesively Bonded Joints. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives 31 (2011) 840–850
- da Silva, L. F. M., Esteves, V. H. C., Chaves, F. J. P.: Fracture Toughness of a Structural Adhesive Under Mixed Mode Loadings. Materialwissenschaft und Werkstofftechnik 42 (2011) 460–470
- Karac, A., Blackman, B. R. K., Cooper, V., Kinloch, A. J., Sanchez, S. R., Teo, W. S., Ivankovic, A.: Modelling the Fracture Behaviour of Adhesively-bonded Joints as a Function of Test Rate. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 78 (2011) 973–989
- Jin, H., Miller, G. M., Sottos, N. R., White, S. R.: Fracture and Fatigue Response of a Self-healing Epoxy Adhesive. Polymer 52 (2011) 1628–1634
- Wong, C. K. Y., Leung, S. Y. Y., Fan, H. B., Yuen, M. M. F.: Synergistic Toughening of Epoxy-Copper Interface Using a Thiol-based Coupling Layer. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology 25 (2011) 2081–2099
- Blackman, B. R. K., Kinloch, A. J., Sanchez, F. S. R., Teo, W. S., Williams, J. G.: The Fracture Behaviour of Structural Adhesives Under High Rates of Testing. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 76 (2009) 2868–2889
- Suarez, J. C., Lopez, F., Miguel, S., Pinilla, P., Herreros, M. A.: Determination of the Mixed-mode Fracture Energy of Elastomeric Structural Adhesives: Evaluation of Debonding Buckling in Fibre-Metal Hybrid Laminates. Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures 32 (2009) 127–140
- Kawashita, L. F., Kinloch, A. J., Moore, D. R., Williams, J. G.: The Influence of Bond Line Thickness and Peel Arm Thickness on Adhesive Fracture Toughness of Rubber Toughened Epoxy-Aluminium Alloy Laminates. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives 28 (2008) 199–210
- Kawashita, L. F., Kinloch, A. J., Moore, D. R., Williams, J. G.: A Critical Investigation of the Use of a Mandrel Peel Method for the Determination of Adhesive Fracture Toughness of Metal-Polymer Laminates. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 73 (2006) 2304–2323
- Hadavinia, H., Kawashita, L., Kinloch, A. J., Moore, D. R., Williams, J. G.: A Numerical Analysis of the Elastic-Plastic Peel Test. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 73 (2006) 2324–2335
- Kawashita, L. F., Moore, D. R., Williams, J. G.: Analysis of Peel Arm Curvature for the Determination of Fracture Toughness in Metal-Polymer Laminates. Journal of Materials Science 40 (2005) 4541–4548
- Kawashita, L. F., Moore, D. R., Williams, J. G.: The Measurement of Cohesive and Interfacial Toughness for Bonded Metal Joints with Epoxy Adhesives. Composite Interfaces 12 (2005) 837–852
- Jyoti, A., Gibson, R. F., Newaz, G. M.: Experimental Studies of Mode I Energy Release Rate in Adhesively Bonded Width Tapered Composite DCB Specimens. Composites Science and Technology 65 (2005) 9–18
- Leung, S. Y. Y., Lam, D. C. C., Luo, S. J., Wong, C. P.: The Role of Water in Delamination in Electronic Packages: Degradation of Interfacial Adhesion. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology 18 (2004) 1103–1121
- Bouchet, J., Roche, A. A., Jacquelin, E.: How do Residual Stresses and Interphase Mechanical Properties Affect Practical Adhesion of Epoxy Diamine/Metallic Substrate Systems? Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology 16 (2002) 1603–1623
- Bouchet, J., Roche, A. A., Jacquelin, E.: The Role of the Polymer/Metal Interphase and its Residual Stresses in the Critical Strain Energy Release Rate (Gc) Determined Using a Three-Point Flexure Test. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology 15 (2001) 345–369
- Meiller, M., Roche, A. A., Sautereau, H.: Tapered Double Cantilever Beam Test Used as a Practical Adhesion Test for Metal/Adhesive/Metal Systems. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology 13 (1999) 773–788
- Phipps, M. A., Pritchard, G., Aboutorabi, A.: The Role of Particle Strength and Filler Volume Fraction in the Fracture of Alumina-Trihydrate Filled Epoxy-resins. Polymer & Polymer Composites 3 (1995) 71–77
- Parry, T. V., Wronski, A. S.: A Technique for the Measurement of Adhesive Fracture Energy by the Blister Method. Journal of Adhesion 37 (1992) 251–260
- Brochu, A. B. W., Evans, G. A., Reichert, W. M.: Mechanical and Cytotoxicity Testing of Acrylic Bone Cement Embedded with Microencapsulated 2-Octyl Cyanoacrylate. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B – Applied Biomaterials 102 (2014) 181–189
- Martiny, P., Lani, F., Kinloch, A. J., Pardoen, T.: A Maximum Stress at a Distance Criterion for the Prediction of Crack Propagation in Adhesively-Bonded Joints. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 97 (2013) 105–135
- Marzi, S., Hesebeck, O., Brede, M., Kleiner, F.: A Rate-Dependent Cohesive Zone Model for Adhesively Bonded Joints Loaded in Mode I. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology 23 (2009) 881–898
- Bland, D. J., Kinloch, A. J., Stolojan, V., Watts, J. F.: Failure Mechanisms in Adhesively Bonded Aluminium: An XPS and PEELS Study. Surface and Interface Analysis 40 (2008) 128–131
- Park, S., Dillard, D. A.: Development of a Simple Mixed-Mode Fracture Test and the Resulting Fracture Energy Envelope for an Adhesive Bond. International Journal of Fracture 148 (2007) 261–271
