Barcol Hardness
| Ein Service der |
|---|

|
| Polymer Service GmbH Merseburg |
| Tel.: +49 3461 30889-50 E-Mail: info@psm-merseburg.de Web: https://www.psm-merseburg.de |
| Unser Weiterbildungsangebot: https://www.psm-merseburg.de/weiterbildung |
| PSM bei Wikipedia: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polymer Service Merseburg |
Barcol Hardness
Basics of Barcol hardness
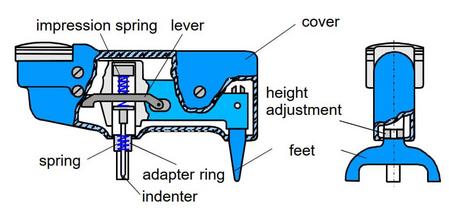
The Barcol hardness measurement method is especially designed for measuring the hardness of glass fibre reinforced plastics, thermosets and hard thermoplastic materials. The valid standards for this test method are ASTM D 2583 [1] and DIN EN 59 [2]. Figure 1 shows the schematic structure of a Barcol hardness tester.
| Figure 1: | Schematic representation of a Barcol hardness tester |
Determining the hardness values
To determine the hardness according to Barcol, the cone indenter made of hardened steel (26°, 0.157 mm diameter) is pressed into the test specimen surface via a spring system. The indentation depth is determined directly via a measuring cell. The hardness is indicated dimensionlessly via a scale from 0 to 100.
The scale value 0 on the dial gauge corresponds to the maximum indentation, i.e. very low hardness, and the value 100 corresponds to practically no indentation, i.e. very high hardness. The calculation equation for the Barcol hardness is:
with indentation depth h ≤ 0.5 mm.
Application of the Barcol hardness test
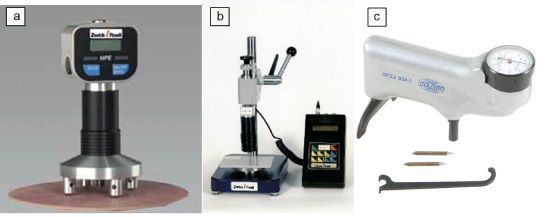
Barcol hardness is used on flat and slightly curved materials, especially for fibre-reinforced plastics, thermosets and hard thermoplastics. Examples of the industrial use of hand-held testers can be found in shipbuilding, aircraft construction, tank construction as well as for hardness testing on plastic pipes and on the blades of wind turbines. Hardness testing can be carried out vertically and horizontally, even at measuring locations that are difficult to access. Figure 2 shows commercially available Barcol hardness testers in the form of mobile hand-held testers and table-top testing systems.
| Figure 2: | Barcol hardness tester: (a) Hand tester Type 3350 from ZwickRoell GmbH & Co. KG, Ulm (b) stationary tester Zwick 3350 and (c) Barcol Tester Elcometer 3101 from Elcometer Instruments GmbH, Aalen |
References
| [1] | ASTM D 2583a (2013): Standard Test Method for Indentation Hardness of Rigid Plastics by Means of a Barcol Impressor (withdrawn 2022) |
| [2] | DIN EN 59 (2016-06): Glass Reinforced Plastics – Determination of Indentation Hardness by Means of a Barcol Hardness Tester |